Now Reading: Demystifying Algorithmic Trading
-
01
Demystifying Algorithmic Trading
Demystifying Algorithmic Trading

Understanding Algorithmic Trading
Have you ever stared at a stock chart, paralyzed by indecision? You see a potential opportunity, but fear holds you back. Or maybe you act too quickly on a surge of excitement, only to watch the market turn against you. The emotional rollercoaster of manual trading, the constant screen time, and the stress of making split-second decisions can be exhausting and costly. It often feels like you’re fighting a losing battle against institutional players with far more resources. What if you could remove the emotion, the hesitation, and the human error from your trading process, and instead rely on pure, data-driven logic?
This is the promise of algorithmic trading. It offers a solution by transforming your trading ideas into a disciplined, automated system that works for you around the clock. By using computer programs to execute trades based on a set of predefined rules, you can approach the markets with a speed, precision, and consistency that is simply impossible for a human to achieve. This guide will walk you through what algorithmic trading is, how it works, its powerful benefits, and the very real risks you need to understand before you begin.
What Exactly Is Algorithmic Trading
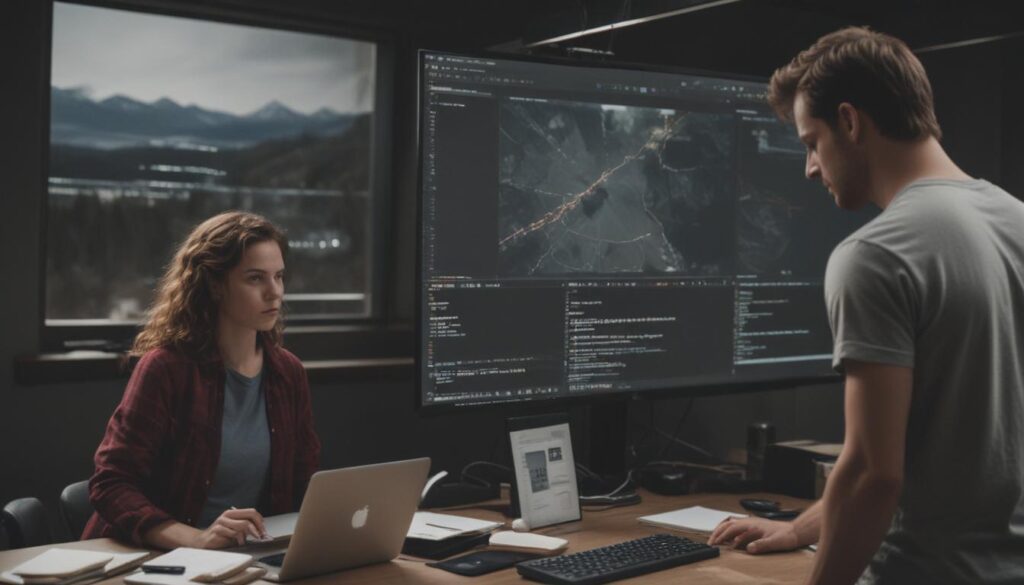
At its core, algorithmic trading, often called algo trading or black-box trading, is the use of computer code to execute trading orders in financial markets. Instead of a person manually clicking “buy” or “sell,” a program is given a specific set of instructions based on variables like price, timing, or volume. When the market conditions meet the criteria defined in the algorithm, the program automatically sends an order to the exchange without any human intervention. This allows for the execution of trades at speeds and frequencies that are beyond human capability.
Think of it as creating a highly specialized and obedient employee. You provide this employee with a very strict rulebook. For example, “If the 50-day moving average of Stock XYZ crosses above the 200-day moving average, buy 100 shares. If it crosses below, sell all shares.” The program will then watch the market tirelessly, 24/7, and execute that exact instruction the moment the condition is met. The complexity of these rules can range from simple conditions like the one above to highly sophisticated quantitative models that analyze millions of data points in real-time.

The Core Components of an Algo Trading System
An algorithmic trading system is more than just a single piece of code. It’s a complete ecosystem designed to identify opportunities and act on them. Understanding its key parts helps demystify the process and reveals where the real work of an algorithmic trader lies.
The Strategy Engine
This is the brain of the entire operation. The strategy engine contains the logic, rules, and calculations that determine when to trade. This is where a trader’s market hypothesis is translated into concrete code. The rules can be based on technical analysis, such as looking for patterns in price charts using indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Bollinger Bands. They could also be based on statistical arbitrage, where the algorithm seeks out temporary price discrepancies between related assets and profits as they return to their normal relationship.
Developing a robust strategy is the most critical and challenging part of algorithmic trading. It involves not only coming up with a potentially profitable idea but also rigorously backtesting it. Backtesting is the process of running your algorithm on historical market data to see how it would have performed in the past. A successful backtest gives you the confidence that your strategy has merit, while a poor one sends you back to the drawing board to refine your logic before risking any real capital.
The Execution Engine
If the strategy engine is the brain, the execution engine is the hands. Once the strategy engine identifies a trading signal, it passes the instruction to the execution engine. This component’s sole job is to communicate with the brokerage or exchange and place the order as efficiently as possible. It connects to the market through an Application Programming Interface (API), which is a gateway that allows different software programs to talk to each other.
Speed and reliability are paramount here. The goal of the execution engine is to minimize slippage, which is the difference between the expected price of a trade and the price at which the trade is actually executed. In fast-moving markets, even a delay of a few milliseconds can significantly impact profitability. This is why professional algorithmic trading firms invest heavily in high-speed servers and direct connections to exchange data centers to ensure their orders are filled first.
Benefits and Risks of Automated Trading
Like any powerful tool, algorithmic trading offers tremendous upside but also comes with significant risks. A balanced understanding is essential for anyone considering this path. It is not a “get rich quick” scheme but a disciplined approach to market participation.
The Powerful Advantages
The most obvious benefit is the elimination of emotional and psychological influences. Algorithms are immune to fear, greed, and panic. They stick to the plan with unwavering discipline, preventing the costly mistakes that human traders often make. This discipline is paired with incredible speed. An algorithm can analyze multiple indicators across dozens of markets and execute an order in a fraction of a second, capitalizing on fleeting opportunities a human would miss.
Furthermore, algorithmic systems enhance efficiency and diversification. A single program can monitor a vast portfolio of assets simultaneously, something no human could ever manage. This allows traders to deploy multiple, uncorrelated strategies across different markets, which can help smooth out returns and reduce overall portfolio risk. Finally, the rigorous process of backtesting a strategy forces a trader to approach the market with quantitative evidence rather than just a gut feeling, leading to a much more informed and systematic trading process.
The Inherent Risks and Challenges
The biggest risk in algorithmic trading is technical failure. A bug in your code, a lost internet connection, or a server outage can lead to catastrophic outcomes, such as placing thousands of erroneous orders or failing to exit a losing position. The history of financial markets is littered with examples of “flash crashes” caused or exacerbated by runaway algorithms. Therefore, robust error handling and failsafes are just as important as the trading logic itself.
Beyond technical glitches lies strategy risk. A strategy that performed brilliantly on historical data may fail spectacularly in live trading because market conditions have changed. This is known as “overfitting,” where a model is too closely tailored to past data and loses its predictive power. The market is a dynamic, evolving entity, and no strategy works forever. Algorithmic traders must constantly monitor their systems’ performance and be prepared to adapt or decommission strategies that are no longer effective. It is an ongoing process of research, testing, and refinement, not a “set it and forget it” solution.