Now Reading: Algorithmic Trading
-
01
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic Trading

Understanding Algorithmic Trading A Guide for Modern Investors
Have you ever watched the stock market, feeling overwhelmed by the lightning-fast price changes and the emotional rollercoaster of making buy or sell decisions? It’s a common frustration for investors who feel they are always one step behind the professional traders and their sophisticated tools. You might hear terms like “high-frequency trading,” “quants,” and “trading bots” and feel that the game is rigged against the individual. You want to make disciplined, data-driven decisions, but the sheer volume of information and the speed required seem impossible to manage manually.
The good news is that there’s a solution that levels the playing field, and it’s more accessible than you might think. This is the world of algorithmic trading, a method that uses computer programs to execute trades based on a set of predefined rules. It’s not just for Wall Street firms anymore. This guide will demystify algorithmic trading, breaking down what it is, how it works, its core benefits and risks, and how you can begin to understand this powerful approach to navigating the financial markets.
What Exactly Is Algorithmic Trading
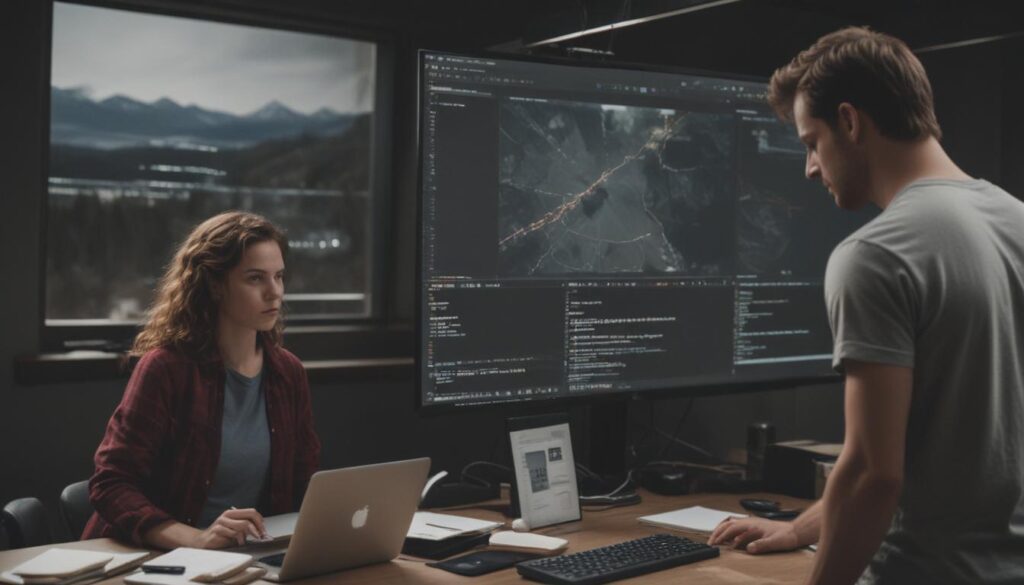
At its core, algorithmic trading, often called “algo trading,” is the practice of using a computer program to place a trade. These programs are built to follow a specific set of instructions, or an algorithm, to make trading decisions that would be impossible for a human to make with the same speed and accuracy. The instructions can be based on various factors, including timing, price movements, trading volume, or complex mathematical models. The primary goal is to automate the trading process, removing human emotion and hesitation from the equation while capitalizing on opportunities that may only exist for a fraction of a second.
Think of an algorithmic trading strategy like a detailed recipe for a chef. The strategy is the recipe, defining every single step. The market data (prices, volume) are the ingredients. The computer is the highly efficient chef who follows the recipe flawlessly, without getting tired or second-guessing the instructions. For example, a simple algorithm might have the rule: “Buy 100 shares of stock XYZ if its price drops by 3% in one hour, and then sell it if the price rises by 2% from the purchase price.” The computer monitors the market constantly and executes this order automatically the moment the conditions are met.
How an Algorithmic Strategy Works in Practice
The creation and deployment of an algorithmic trading strategy involve a structured process that moves from a simple idea to a live, automated system. It all begins with identifying a market inefficiency or a pattern that can be translated into a set of objective rules. This idea could come from technical analysis, statistical arbitrage, or fundamental data. Once you have a hypothesis, such as “stocks tend to rise after their 50-day moving average crosses above their 200-day moving average,” the real work of building the algorithm begins.
The next critical step is backtesting. This is where the trading strategy is rigorously tested against historical market data to see how it would have performed in the past. Backtesting helps traders identify flaws in their logic, optimize parameters, and get a realistic estimate of the strategy’s potential profitability and risk. If a strategy performs well in backtesting, it might be moved to paper trading (simulated trading with real-time data) to see how it behaves in a live market environment without risking real capital. Only after it proves itself in these stages is the algorithm deployed to trade with real money, where it will automatically scan the markets and execute trades according to its programming.
A Simple Algorithmic Trading Strategy Example
To make this concept more concrete, let’s look at a classic strategy based on moving averages, which are used to identify the direction of a market trend. A popular strategy is the “Golden Cross,” which uses two moving averages: a short-term one (like the 50-day) and a long-term one (like the 200-day). The logic is that when the short-term trend momentum overtakes the long-term trend, it signals a potential upward breakout.
The algorithm for a Golden Cross strategy would have two simple, unbreakable rules. Rule 1: Buy Signal: Execute a buy order for a specific asset when its 50-day moving average crosses from below to above its 200-day moving average. Rule 2: Sell Signal: Execute a sell order for that asset when its 50-day moving average crosses from above to below its 200-day moving average (a pattern known as a “Death Cross”). This strategy is entirely mechanical. The algorithm isn’t “thinking” about the news or the economy; it is only monitoring the two moving average values and acting instantly when its conditions are met, ensuring disciplined entry and exit points.

The Advantages and Disadvantages of Algorithmic Trading
One of the most significant advantages of algorithmic trading is its incredible speed. An algorithm can analyze market data and execute an order in microseconds, far faster than any human. This speed is crucial for strategies that rely on capturing small price discrepancies. Furthermore, algorithms eliminate emotional and psychological biases. Fear and greed are powerful forces that often lead to poor manual trading decisions, such as selling in a panic or holding on to a losing trade for too long. An algorithm sticks to its rules, ensuring a disciplined approach 24/7 without getting tired or emotional.
However, algorithmic trading is not without its risks. A poorly designed or buggy algorithm can lead to disastrous losses in a very short amount of time. This is why rigorous backtesting and monitoring are so important. Another risk is “overfitting,” where a strategy is so finely tuned to past historical data that it performs beautifully in tests but fails in the live market, which is always evolving. Finally, events like “flash crashes,” where automated systems react to each other and cause a sudden, massive market drop, highlight the systemic risks when a large portion of the market is driven by similar algorithmic logic.
Is Algorithmic Trading Right for You
Deciding whether to explore algorithmic trading depends heavily on your skills, interests, and investing philosophy. It is not a “get rich quick” scheme but a systematic approach that requires a blend of market knowledge, strategic thinking, and technical aptitude. If you enjoy analyzing data, building systems, and testing hypotheses in a disciplined manner, you may find algorithmic trading to be a rewarding field. It’s for the investor who would rather spend their time developing and refining a robust strategy than being glued to a screen reacting to every market tick.
For those intrigued by the concept, the journey begins with education. Start by learning the fundamentals of financial markets and the core principles of popular trading strategies. You don’t necessarily need to be a master coder, as many modern platforms offer tools to build and test algorithms with minimal programming. The key is to start small, test thoroughly, and understand that even an automated system requires a smart and vigilant human operator behind it. By doing so, you can harness the power of automation to become a more disciplined and effective investor.