Now Reading: Algo Trading Demystified
-
01
Algo Trading Demystified
Algo Trading Demystified

Understanding Algorithmic Trading A Guide for the Modern Investor
Have you ever watched the fast-paced stock market and felt like you were always one step behind? It can feel like an impossible race against powerful computers, where every move you make is just a little too slow. The constant pressure to act instantly, mixed with the emotional stress of watching your investments fluctuate, can be draining and lead to poor decisions. Many individual investors feel outmatched by large financial firms using complex algorithms, creating a sense that the game isn’t fair. This feeling of being overwhelmed is a major hurdle for anyone wanting to trade successfully in today’s digital financial markets.
The answer isn’t to try and trade faster, but to trade smarter. This is where algorithmic trading, often called algo trading, changes the game. It provides you with the tools to level the playing field, allowing you to use technology to execute your trading plan with incredible speed, discipline, and precision. This guide will make the world of algorithmic trading easy to understand. We will break down what it is, how it works, and the most important advantages and disadvantages. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of this powerful trading method and whether it’s the right choice for you.
What Is Algorithmic Trading
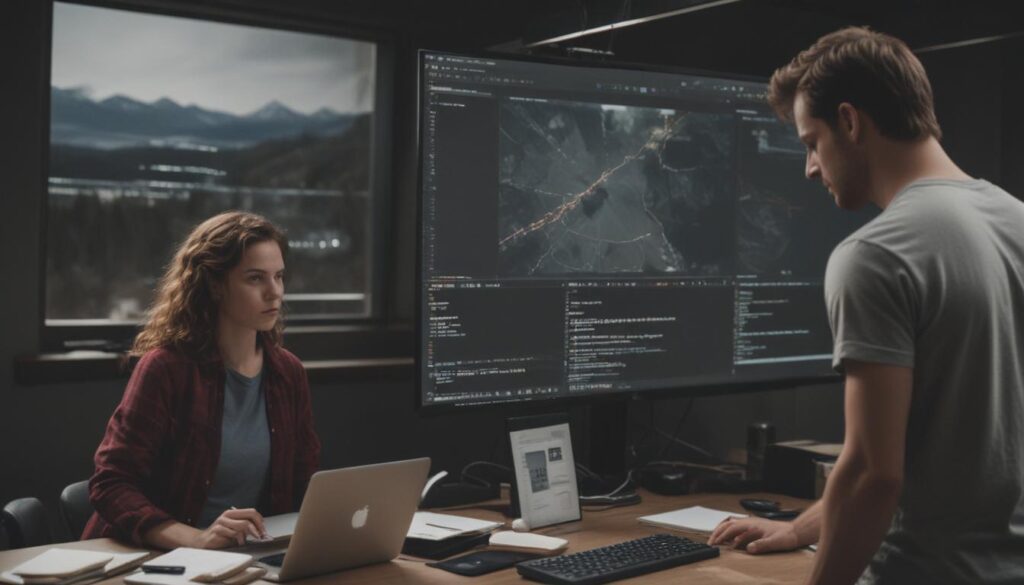
At its heart, algorithmic trading is the use of a computer program to automatically execute trades based on a set of predefined rules. Instead of a person manually clicking the “buy” or “sell” button, a computer algorithm monitors the market and acts on its own when certain conditions are met. These rules can be simple or complex, based on factors like price, time, trading volume, or other technical indicators. Think of it as giving your computer a detailed instruction manual for trading, which it then follows with perfect speed and consistency.
A huge benefit of this approach is that it removes human emotion from the equation. Emotions like fear during a market dip or greed during a rally are often the biggest cause of trading mistakes. An algorithm doesn’t feel panic or excitement; it only follows the instructions it was given. Furthermore, it can analyze huge amounts of data across multiple markets at once, something no human could ever do. Whether the rule is as simple as “buy 100 shares of a stock when it crosses its average price” or a highly complex strategy, algo trading turns your plan into an automated, real-time operation.

How Does Algorithmic Trading Work
The process of algorithmic trading involves a few key parts working together. It all begins with a trading strategy, which is the logic behind all the decisions. This strategy is then translated into computer code to create the “algorithm.” This program is connected to a live feed of market data, giving it a constant stream of information like stock prices, trading volume, and order updates. The algorithm continuously checks this incoming data against its programmed rules.
When the market data matches the criteria of the strategy, the program instantly generates a trade order and sends it to a brokerage to be executed. This all happens in a fraction of a second, allowing the system to take advantage of small opportunities a human trader would likely miss. To make sure a strategy is solid before using real money, traders perform backtesting. This means running the algorithm on historical market data to see how it would have performed in the past. If the results look good, the strategy can be deployed in the live market, often with a small amount of money at first to test its real-world performance. Continuous monitoring is essential, as algorithms often need to be adjusted to stay effective as market conditions evolve.
The Pros and Cons of Algorithmic Trading
One of the biggest benefits of algorithmic trading is its incredible speed. Orders are executed in milliseconds at the best available prices, which helps reduce costs from price slippage. This is matched by its accuracy; an automated system won’t make a “fat-finger” error like accidentally typing an extra zero on a trade order. Algorithms can also work around the clock without getting tired, scanning global markets for opportunities while you are away or asleep. Finally, the ability to backtest a strategy gives you statistical proof of its potential effectiveness before you risk a single dollar.
However, algorithmic trading also comes with significant challenges. The main drawback is its technical complexity. To build and manage a trading algorithm, you need skills in programming, statistics, and financial markets. A tiny bug or error in the code could cause major and very rapid financial losses. These systems also demand constant monitoring. Although they are automated, they are not “set and forget.” A strategy that was profitable yesterday might become useless or even harmful if market dynamics change. There is also the risk of over-optimization, where an algorithm is tailored so perfectly to past data that it fails to perform well in the live, unpredictable market.